Organizational Structure for LeSS Huge
Scale is often accompanied with additional organizational structure. Before we explore the typical additional structure, we’d like to stress that scale doesn’t have to mean additional structure. Additional structure usually causes narrower responsibilities which paves the way for loads of organizational dysfunction and politics. Keep organizational design simple.
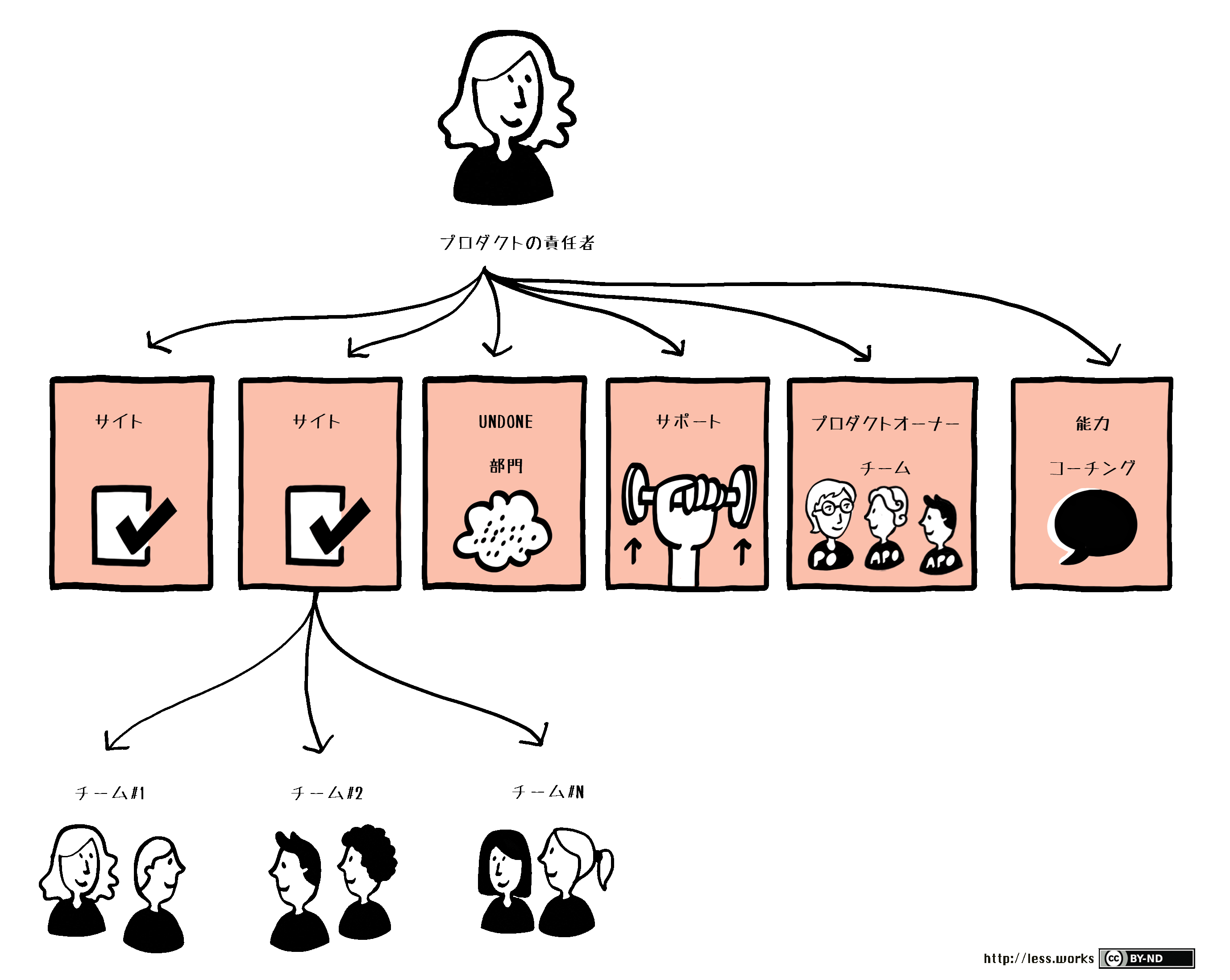
With that caveat, a LeSS Huge structure is built on top of the LeSS structure. A typical LeSS Huge organizational chart looks like Figure 1:
Let’s examine parts that differ from the LeSS organization:
- Teams in sites—LeSS Huge is usually multi-site, and the line organization tends to stay local to the site. Avoid making the requirement areas the line organization as that would lead to more permanent or rigid (anti-adaptive) requirement areas than needed.
- Product Owner Team—Conceptually the same as in a LeSS structure. The team is larger as it includes all the Area Product Owners. In huge LeSS Huge groups, the Product Owner Team has additional structure or sub-teams based on the Requirement Areas.
- Undone Department—Also conceptually the same as in a LeSS struture. In LeSS Huge groups there tend to be bigger Undone departments and it takes a longer time to get rid of them. In huge LeSS Huge groups, there will be additional structure in the Undone department.
- Support—This department provides development environment support for the teams. In LeSS the teams support each other without the need for a separate group. But in typical LeSS Huge organizations they do ‘centralize’ some support, usually because of the massive volume of work. Still, this department should be as small as possible with the attitude “How can we help?” rather than “Take it this way!” Why? Support groups often end up taking over responsibilities from the teams and become huge ever growing pulsating abominations controlling rather than supporting the teams.
Common support groups include configuration management, laboratory support, continuous-integration system support, or operations support. - Competence and Coaching—Software is created by people. Improving people improves products. This seems obvious, yet we rarely see organizations that are truly committed to relentlessly training and coaching of their people. LeSS Huge organizations have a dedicated training and coaching department which is essential for continuous improvement.
The competence and coaching department focuses on three things:- observation (Go See)
- training
- coaching
The competence and coaching group consists of skillful practitioner-experts who actively Go See and observe how people work. They pair up and work with people to discover their training needs. People don’t ask for training on subjects they don’t know exist or for skills they don’t know are weak.
Coaching is key! It is the most effective way to help teams improve. Coaches work with or in teams. They observe, pair, shadow, and question. They give observations, feedback, ideas and examples on how the team can improve. Coaching happens on three levels: (1) organizational, (2) team, and (3) technical. All these levels are important. We have yet to see a successful LeSS adoption without active coaching.